Mouth Cyst Pops Up Now and Again
Growths can originate in any type of tissue in and effectually the mouth, including connective tissues, os, muscle, and nerve. Growths most commonly course on the
-
Lips
-
Sides of the tongue
-
Floor of the oral cavity
-
Back portion of the roof of the rima oris (soft palate)
Some growths cause hurting or irritation.
Mouth growths tin be
-
Noncancerous (benign)
-
Precancerous (dysplastic)
-
Malignant (malignant)
Most mouth growths are noncancerous.
A diverseness of noncancerous growths may occur in and around the oral cavity. A persistent lump or raised area on the gums (gingiva) should be evaluated by a dentist. Such a lump may be acquired by a gum or tooth abscess or by irritation. But, because any unusual growths in or around the rima oris tin can be cancer, the growths should exist checked by a dr. or dentist without delay.
Noncancerous growths due to irritation are relatively common and, if necessary, can be removed by surgery. In 10 to forty% of people, noncancerous growths on the gums reappear considering the irritant remains. Occasionally such irritation, particularly if it persists over a long period of time, tin atomic number 82 to precancerous changes.
Thrush Symptoms 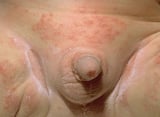 is a yeast infection of moist areas of the pare and other moist areas (such equally the mouth and vagina). In the mouth it often appears as whitish, cheeselike patches. Thrush sticks tightly to the mucous membranes and when wiped away, leaves a red patch. Thrush is near mutual among people with diabetes or a suppressed immune system and in those who are taking antibiotics.
is a yeast infection of moist areas of the pare and other moist areas (such equally the mouth and vagina). In the mouth it often appears as whitish, cheeselike patches. Thrush sticks tightly to the mucous membranes and when wiped away, leaves a red patch. Thrush is near mutual among people with diabetes or a suppressed immune system and in those who are taking antibiotics.
Cysts (hollow, fluid-filled swellings) of many types cause jaw pain and swelling. Often they are side by side to an impacted wisdom tooth and tin can destroy considerable areas of the jawbone equally they expand. Sure types of cysts are more likely to recur after surgical removal. Various types of cysts may develop in the floor of the rima oris. Often, cysts are surgically removed because they brand swallowing uncomfortable or because they are unattractive. By far the most mutual cyst occurs in the lip and is called a mucocele or mucus retention cyst. It is commonly the result of accidentally bitter the (lower) lip and occurs when saliva draining into the mouth from a pocket-sized salivary gland is blocked. Most mucoceles disappear in a week or two merely can be surgically removed if annoying.
Odontomas are overgrowths of tooth-forming cells that expect like either modest, misshapen extra teeth or a large mass of molar material. In children, they may become in the way of normal teeth coming in. In adults, they may push teeth out of alignment. If odontomas abound large, they may cause the upper or lower jaw to get enlarged equally well. They are usually removed surgically.
Nigh (75 to 80%) salivary gland tumors are noncancerous, slow-growing, and painless. They usually occur as a single, soft, movable lump beneath normal-looking skin or under the lining (mucosa) of the within of the oral fissure. Occasionally, when hollow and fluid-filled, they are business firm. The most common blazon (called a mixed tumor or pleomorphic adenoma) occurs mainly in women older than 40. This blazon can become malignant and is removed surgically. Unless completely removed, this blazon of tumor is likely to grow dorsum. Other types of noncancerous tumors are also removed surgically but are much less likely to become malignant or to grow back once removed.
White, ruby-red, or mixed white-reddish areas that are non easily wiped abroad, persist for more than than two weeks, and are not definable as some other condition may exist precancerous. The same hazard factors are involved in precancerous changes as in cancerous growths, and precancerous changes may become malignant if not removed.
Leukoplakia is a flat white spot that may develop when the moist lining of the mouth (oral mucosa) is irritated for a long period. The irritated spot appears white because it has a thickened layer of keratin—the same material that covers the skin and usually is less arable in the lining of the mouth.
Erythroplakia is a red and apartment or worn-away area that results when the lining of the mouth thins. The area appears red because the underlying capillaries are more visible. Erythroplakia is a much more ominous predictor of oral cancer than leukoplakia.
Mixed white-crimson areas contain both leukoplakia and erythroplakia and too may become cancer over fourth dimension.
People who utilize tobacco, alcohol, or both are at much greater take a chance (up to fifteen times) of oral cancer Mouth and Throat Cancer Mouth and pharynx cancers are cancers that originate on the lips, the roof, sides, or flooring of the mouth, natural language, tonsils, or back of the throat. Oral cavity and throat cancers may look like open sores... read more  . For those who utilise chewing tobacco and snuff, the insides of the cheeks and lips are common sites of oral cancer. In other people, the most mutual sites for oral cancer include the sides of the tongue, the flooring of the mouth, and the throat. Cancers caused past oral infection with human papillomavirus Human being Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection Man papillomavirus (HPV) causes warts. Some types of HPV cause skin warts, and other types crusade genital warts (growths in or around the vagina, penis, or rectum). Infection with some HPV... read more than
. For those who utilise chewing tobacco and snuff, the insides of the cheeks and lips are common sites of oral cancer. In other people, the most mutual sites for oral cancer include the sides of the tongue, the flooring of the mouth, and the throat. Cancers caused past oral infection with human papillomavirus Human being Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection Man papillomavirus (HPV) causes warts. Some types of HPV cause skin warts, and other types crusade genital warts (growths in or around the vagina, penis, or rectum). Infection with some HPV... read more than 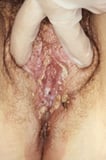 (HPV), especially type 16, unremarkably occur at the back of the pharynx, base of operations of natural language, and tonsils. HPV infection is now a more common cause of cancers at these sites than tobacco. Rarely, cancers plant in the oral cavity region have spread there from other parts of the body, such every bit the lungs, breast, or prostate.
(HPV), especially type 16, unremarkably occur at the back of the pharynx, base of operations of natural language, and tonsils. HPV infection is now a more common cause of cancers at these sites than tobacco. Rarely, cancers plant in the oral cavity region have spread there from other parts of the body, such every bit the lungs, breast, or prostate.
Oral cancer can accept many different appearances but typically resembles precancerous lesions (for case, white, red, or mixed white-ruddy areas that are not easily wiped away).
The following information can help people decide when a doctor'due south evaluation is needed and help them know what to expect during the evaluation.
Sure symptoms and characteristics are crusade for concern. They include
-
Weight loss
-
Firm lump in the cervix
-
A sore throat that volition non become away
-
Difficulty swallowing
People with a mouth growth that does not go abroad in a week or 2 should come across their dr. or dentist when user-friendly. Warning signs suggest a higher risk of cancer, and people with warning signs (particularly those who use tobacco) should not put off being evaluated.
Because oral cancer frequently causes no symptoms early on, it is important for people to take a yearly examination of the mouth. Such an examination can be done during an annual dental bank check-up.
Doctors offset ask questions about the person'south symptoms and medical history. Doctors and so do a physical examination. What they find during the history and physical test can help suggest a cause of the oral fissure growth.
Doctors ask people about how long the growth has been present, whether it is painful, and whether there was whatsoever injury to the surface area (for instance, biting a cheek or scraping by a sharp molar border or dental restoration). Other things they ask about include
-
The amount and elapsing of employ of booze and tobacco
-
Whether the person has lost weight or been feeling generally ill
-
How oft the person has oral sex and the number of sexual contacts with whom they engage in oral sexual practice
The physical examination focuses on the mouth and neck. Doctors look carefully at all areas of the mouth and pharynx, including under the tongue. They feel the sides of the neck for swollen glands (lymph nodes), which indicate possible cancer or chronic infection.
If a growth has the appearance of thrush, doctors examine scrapings nether a microscope. For other growths that accept lasted longer than a few weeks, well-nigh doctors recommend removing all or function of the growth for examination in a laboratory (biopsy). Biopsy is often necessary to make sure a growth is noncancerous.
-
Treatment depends on the cause
Handling differs depending on the crusade, cosmetic effects or other symptoms, and possibility of cancerous transformation of the growth.
-
Most oral cavity growths are noncancerous.
-
Warts, yeast infections, and repeated trauma (such every bit biting or rubbing against a precipitous tooth edge) are common causes of noncancerous growths.
-
Use of booze and tobacco and oral man papillomavirus (HPV) infection are hazard factors for oral cancer.
-
Because cancerous growths are hard to recognize by their appearance, doctors often recommend a biopsy.
The following is an English-language resource that may be useful. Please note that THE Manual is not responsible for the content of this resource.
-
MouthHealthy.org: Provides information on oral health, including nutrition and guidance on selecting products that behave the American Dental Association'due south seal of approval. There is as well advice on finding a dentist and how and when to see ane.
stinsonmilatichated.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/mouth-and-dental-disorders/symptoms-of-oral-and-dental-disorders/mouth-growths
0 Response to "Mouth Cyst Pops Up Now and Again"
Yorum Gönder